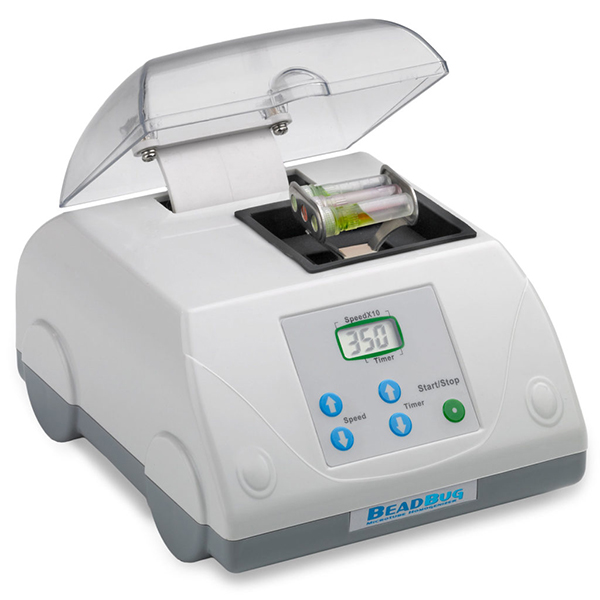
Small Laboratory Homogenizers for DNA/RNA Extraction & Sample Lysis
Small laboratory homogenizers provide high-energy mechanical disruption for small-volume samples in a compact,
benchtop footprint. These instruments are designed to lyse cells, break down tissues, and disperse solid or
semi-solid material in 1.5–2.0 mL tubes or similar vessels. For molecular biology, genomics, proteomics, and
microbiology labs, a
small laboratory homogenizer delivers faster, more reproducible results than
manual grinding or basic vortex mixing.
ARES Scientific offers a curated selection of
benchtop homogenizers, including
microtube homogenizers and
bead mill homogenizers engineered for demanding DNA/RNA extraction,
sample lysis, and tissue homogenization workflows. These compact systems fit easily into crowded lab spaces while
providing the power, speed, and consistency required for high-quality downstream analysis.
Applications for Small Laboratory Homogenizers
Small homogenizers are used whenever you need efficient, repeatable disruption of limited sample volumes. Typical
applications include:
- DNA and RNA extraction: Rapid lysis of cells and tissues for nucleic acid purification.
- Protein extraction: Homogenization of tissues and pellets for Western blot, ELISA, or mass spectrometry workflows.
- Microbial lysis: Disruption of bacterial, yeast, and fungal cells, including tough Gram-positive strains.
- Plant and seed disruption: Grinding of leaves, seeds, and other plant material for genomics and metabolomics.
- Tissue homogenization: Processing liver, brain, muscle, and other soft tissues for biochemical analysis.
- Sample preparation for assays: Uniform dispersion of solids and viscous samples prior to quantitative testing.
Types of Small Homogenizers We Offer
Different laboratories require different homogenization technologies. Small laboratory homogenizers available through
ARES Scientific include:
- Bead mill homogenizers: Use high-speed shaking with beads in sealed tubes for powerful cell disruption and tissue lysis.
- Microtube homogenizers: Compact units optimized for 1.5–2.0 mL tubes, ideal for low-volume sample lysis at the bench.
- High-speed benchtop homogenizers: Designed for rapid processing of multiple samples in parallel for higher throughput.
Many systems are compatible with a range of bead types and tube formats so you can tailor the homogenization protocol
to your sample type, from soft tissues and cultured cells to plant material and microbial pellets.
How to Choose a Small Laboratory Homogenizer
When selecting a
small homogenizer for your lab, consider the following factors:
- Sample type and hardness: Tough tissues, seeds, and spores typically require high-energy bead mill homogenizers.
- Throughput requirements: Choose capacity (number of tubes per run) to match your daily sample volume.
- Tube format: Confirm compatibility with your preferred 1.5–2.0 mL microtubes or screw-cap tubes.
- Speed and control: Adjustable speed and time settings allow optimization for delicate and challenging samples.
- Contamination control: Sealed-tube bead beating reduces aerosolization and cross-contamination risk.
- Footprint and environment: Compact designs fit easily in biosafety cabinets, cold rooms, or crowded benches.
Integrating Small Homogenizers into Your Workflow
Small laboratory homogenizers pair naturally with other sample-preparation tools such as
microcentrifuges,
pipettes, and cold storage. After homogenization, samples can move directly into extraction kits, spin columns, or
downstream analytical instruments, helping streamline your lab’s DNA/RNA, protein, and microbiology workflows.
By standardizing homogenization with a dedicated benchtop system, labs improve reproducibility, reduce hands-on time,
and increase overall throughput.
For larger-scale or specialty applications, ARES Scientific also supports additional
laboratory homogenizers and cell disruption systems
beyond the small-format instruments featured in this category.
Small Laboratory Homogenizer FAQ
What is a small laboratory homogenizer?
A small laboratory homogenizer is a compact benchtop instrument designed to disrupt cells, tissues, and other
solid or semi-solid samples in small-volume tubes. It provides controlled mechanical energy for sample lysis,
nucleic acid extraction, and tissue homogenization.
When should I use a bead mill homogenizer instead of a vortex mixer?
Use a bead mill homogenizer when you need true cell disruption or tissue breakdown, especially for tough samples.
Vortex mixers can mix and resuspend pellets, but they do not provide the same level of mechanical force for DNA/RNA
extraction or microbial lysis.
What sample types can small homogenizers handle?
Small homogenizers can process cultured cells, animal tissues, plant leaves and seeds, bacterial pellets, yeast, fungi,
soil microbes, and other challenging biological samples, depending on the beads and tubes used.
How much volume can small homogenizers process?
Most small laboratory homogenizers are optimized for 1.5–2.0 mL microtubes. Some models support multiple tubes per run
to increase throughput while still working with low sample volumes.
Are small homogenizers suitable for DNA and RNA extraction workflows?
Yes. They are widely used at the front end of DNA/RNA extraction workflows to lyse cells and tissues, releasing
nucleic acids for subsequent purification using spin columns or magnetic bead kits.
Can small homogenizers be used in a biosafety cabinet or cold room?
Many compact homogenizers are suitable for use inside biosafety cabinets or cold rooms, provided there is adequate
space and power. Always follow the manufacturer’s environmental and safety guidelines.
What maintenance do small laboratory homogenizers require?
Routine maintenance typically includes wiping down accessible surfaces, inspecting tube holders, and ensuring
that tubes and beads are used according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Most units require very little
ongoing service under normal conditions.
How do I reduce cross-contamination when homogenizing multiple samples?
Use sealed screw-cap tubes, choose appropriate beads for your sample type, and avoid reusing tubes or beads
between samples. Bead mill homogenizers with sealed tubes greatly minimize aerosol formation and carryover.