In the high-stakes realm of pharmaceutical manufacturing and distribution, maintaining the integrity of products through meticulous temperature and humidity control is critically important. From the moment created to the point it’s delivered to the end user, a pharmaceutical product navigates a complex cold chain—a sequence of temperature-controlled environments designed to preserve its quality and efficacy. This journey underscores the critical need for pharmaceutical manufacturers to qualify temperature-controlled storage areas, carefully maintain refrigeration equipment, and regularly calibrate monitoring sensors, all in compliance with stringent regulatory standards.
The cold chain’s multi-stage process demands precise and reliable monitoring at each phase to prevent any compromise to the product’s quality and integrity. Different stakeholders within the chain, from manufacturers to end users, require tailored information from temperature-monitoring devices. For instance, while the end recipient may primarily need to know about any temperature excursions, the logistics provider and the manufacturer will seek detailed insights into the cause of such deviations. This complex interplay of requirements emphasizes the need for a versatile and continuous temperature monitoring system that caters to the diverse needs of all parties.
Key Aspects of Temperature and Humidity Control in Pharmaceuticals
- Qualification of Storage Areas: Checking that storage environments meet the necessary temperature and humidity specifications.
- Continuous Monitoring: Implementing systems to continuously monitor and record environmental conditions.
- Equipment Maintenance: Regular upkeep and calibration of refrigeration and monitoring equipment to ensure accuracy and reliability.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to guidelines set by bodies such as the WHO, IATA, ICH, as well as national agencies like the US FDA and the MHRA.
The Cold Chain’s Complexity:
- Multiple Stages: Pharmaceuticals pass through various temperature-controlled stages, from manufacturing to delivery.
- Stakeholder Needs: Different information is required by manufacturers, logistics providers, and end users.
- Quality Risk Management: A systematic approach to managing risks to product quality across its lifecycle, as defined by the ICH and supported by regulatory updates.
Regulatory Framework:
- National and International Guidelines: Regulations and guidelines from the USFDA, EMA, MHRA, IATA, ICH, and WHO shape the industry’s temperature control standards.
- Comprehensive Monitoring: Manufacturers are required to undertake extensive temperature monitoring, documented in quality agreements with supply chain partners.
Innovations in Monitoring:
- Static and Dynamic Monitoring: Solutions for both the static phases of storage and the dynamic phases of transit.
- Advanced Technologies: Systems equipped with high-performance sensors for active temperature control and real-time monitoring.

Global Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape for temperature and humidity control in the pharmaceutical industry is shaped by various international and national bodies. Key among these are the World Health Organization (WHO), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH).
ICH Guidelines
The ICH, through its Q series of quality guidelines, provides a harmonized framework that influences global regulatory policies. Specifically, ICH Q1A(R2) on stability testing outlines the importance of storing pharmaceutical products under conditions that test their thermal stability and humidity resistance, thereby indirectly setting a precedent for temperature and humidity control.
FDA Regulations
In the United States, the FDA’s Code of Federal Regulations Title 21, Part 211, specifically sections 211.42, 211.46, and 211.142, lay down the requirements for temperature and humidity control in pharmaceutical manufacturing and storage facilities. These regulations mandate that operations be performed in controlled areas to prevent contamination and mix-ups, and that drug products be stored under appropriate conditions of temperature and humidity to maintain their identity, strength, quality, and purity.
EMA Guidelines
The European Union’s EudraLex Volume 4, which encompasses the Good Manufacturing Practice guidelines for pharmaceutical products, specifies the requirements for temperature and humidity control. Chapters and annexes within this volume, such as Chapter 3 on premises and equipment and Annex 1 on the manufacture of sterile medicinal products, highlight the necessity of maintaining appropriate environmental conditions, including temperature and humidity, to not adversely affect product quality or the accurate functioning of equipment.
WHO Guidelines
The WHO provides guidance on good storage and distribution practices for pharmaceutical products, emphasizing the need for temperature and humidity control in storage areas to ensure product stability and integrity. These guidelines serve as a reference standard for many countries, especially in regions without a well-developed regulatory framework.
Specific Regulatory Requirements
- Design and Validation: Regulatory bodies require that pharmaceutical facilities’ HVAC systems be designed to maintain predefined temperature and humidity ranges. This includes the validation and qualification of these systems to demonstrate consistent control over environmental conditions.
- Monitoring and Alarm Systems: Continuous monitoring of temperature and humidity with calibrated instruments is mandated, with clear specifications for alarm limits and responses to excursions beyond these limits.
- Documentation and Records: Detailed records of temperature and humidity monitoring are mandatory for compliance. These records must be available for review during inspections and audits, demonstrating control over environmental conditions.
- Risk Management: Regulations emphasize a risk-based approach to managing temperature and humidity control, including the assessment of potential impacts on product quality and the implementation of mitigation strategies.
- Product-Specific Requirements: Certain pharmaceutical products, such as biologics, vaccines, and certain chemicals, may have specific temperature and humidity requirements. Regulatory submissions for these products must include stability data supporting the proposed storage conditions.
Ensuring the integrity and efficacy of pharmaceuticals from production to delivery is vital, and this is where stringent temperature monitoring comes into play. The pharmaceutical industry adheres to specific temperature guidelines to preserve the quality of its products. These guidelines vary based on the nature of the pharmaceuticals and the regulations of authoritative bodies such as the FDA, EMA, and WHO.

Key Aspects of Temperature Monitoring in Pharmaceuticals
- Defined Temperature Ranges: Different pharmaceuticals require distinct storage temperatures. Vaccines and biologics, for instance, often need to be refrigerated within a specific range, typically 2 to 8 degrees Celsius (35 to 46 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Consistent Monitoring and Data Logging: Continuous temperature tracking with precise instruments is crucial. This process involves regular data recording to maintain a historical log for quality assurance and compliance purposes.
- Alert Mechanisms: Implementing alarm systems to notify personnel of temperature deviations allows for timely corrective measures and prevents product spoilage.
- Equipment Calibration: Ensuring the monitoring equipment is regularly calibrated and validated enables accuracy and reliability.
- Storage Area Mapping: Conducting temperature mapping and validation to guarantee even temperature distribution within storage spaces is essential.
- Regulatory Adherence: Complying with the stipulated guidelines of regulatory authorities is compulsory, encompassing specific documentation and reporting protocols.
- Staff Training and SOPs: Educating staff on proper storage and handling procedures, including the use of monitoring equipment, and establishing standard operating procedures for addressing temperature excursions are critical.
- Emergency Preparedness: Having contingency plans for power outages or equipment failures, including backup power sources and alternative storage solutions, is also important.

Thermometers in the Pharmaceutical Sector
The pharmaceutical industry relies on various thermometers for accurate temperature monitoring:
- Digital Thermometers: Known for their precision, ease of use, and data-recording capabilities.
- Infrared (IR) Thermometers: Ideal for non-contact temperature measurements.
- Data Loggers: Useful for tracking temperature over time, especially in storage and during transport.
- Liquid-in-glass Thermometers: Although traditional, their use is decreasing due to potential breakage and mercury hazards.
- Thermocouples and Bimetallic Thermometers: Suited for industrial applications and specific temperature measurement needs.
- Chart Recorders and Thermographs: Provide continuous temperature documentation, which is crucial for storage environment monitoring.
Continuous Temperature Monitoring Devices:
These systems are designed for the continuous surveillance of pharmaceutical storage temperatures, featuring:
- 24/7 Monitoring: Continuous temperature recording at predetermined intervals.
- Alert Systems: Notifications for any temperature deviations to prompt immediate action.
- Data Logging: Essential for regulatory compliance and quality assurance.
- Remote Access: Modern systems offer remote monitoring capabilities for convenience and efficiency.
Optimal Pharmacy Temperatures:
- Room Temperature Storage: Typically between 20 C to 25 C (68 to 77 F) for most medications.
- Refrigerated Storage: For certain vaccines and biologics, between 2 to 8 C (35 to 46 F) is required.
- Freezer Storage: Some products need to be stored at minus 25 to minus 15 C (minus 13 to 5 F).
Pharmacy Refrigerator Temperature Checks:
- Use a Calibrated Thermometer: Ensure it’s designed for refrigerator use.
- Correct Placement: Position it away from cooling elements, doors, and walls for accurate readings.
- Regular Monitoring: Check the temperature daily and maintain a log for compliance and quality control.
Routine Checks and Acceptable Ranges:
- Daily Checks: It’s crucial to monitor and document the temperatures of pharmacy refrigerators and freezers daily.
- Acceptable Ranges: For drug refrigerators, maintaining a temperature between 2 to 8 C (35 to 46 F) is essential.
Implementing Best Practices for Temperature Control
Despite adherence to standard temperature guidelines, unforeseen circumstances like heat waves, power outages, or equipment malfunctions can pose significant risks. To mitigate these, several best practices are recommended:
- Airflow Management: Proper ventilation and the use of fans can help dissipate unwanted heat, maintaining a stable environment.
- Secure Packaging: Ensuring medications are properly sealed and packaged can protect them from temperature fluctuations.
- Air Conditioning: Regular maintenance of air conditioning systems is essential to combat high temperature conditions.
- Strategic Placement: Organizing storage to facilitate airflow between packages can prevent heat accumulation.
Furthermore, maintaining temperature integrity during transportation and delivery is critical. Compliance with WHO guidelines, including accurate temperature monitoring and annual calibration against certified standards, ensures the safe transit of pharmaceuticals.
The Significance of Humidity Monitoring
Humidity levels within pharmaceutical storage areas are equally important, with the WHO recommending relative humidity levels to be 60 percent or lower. High humidity can compromise medication quality, leading to degradation or reduced efficacy. To effectively manage humidity, several strategies are recommended:
- Designated Sealed Areas: Storage areas requiring low humidity levels should be well-sealed and isolated from higher humidity zones.
- Moisture Control: Preventing moisture from entering HVAC systems and employing dehumidifiers can help maintain desired humidity levels.
- Humidity Source Management: Avoiding humidifiers due to potential microbial contamination risks is advisable. Instead, alternatives like steam injection can be employed, ensuring no harmful chemicals compromise the pharmaceutical products.
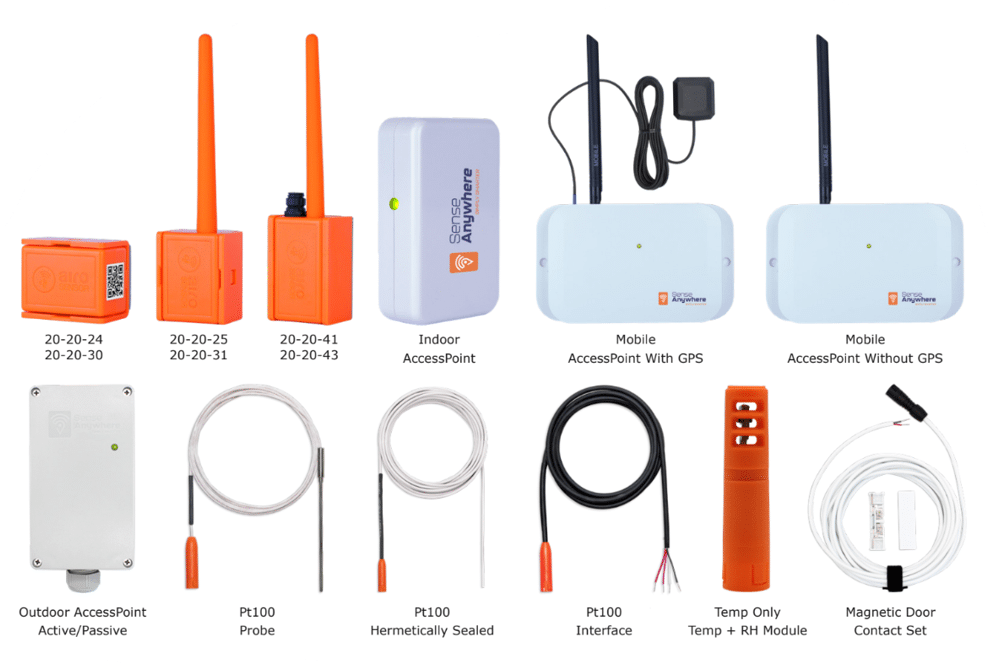
Enhancing Facility Management with SenseAnywhere: A Comprehensive Overview
In today’s fast-paced medical and pharmaceutical sectors, maintaining the integrity of temperature-sensitive products is paramount. SenseAnywhere emerges as a beacon of innovation in environmental monitoring, offering an array of products designed to ensure the utmost precision, reliability, and ease of use. This article delves deep into the functionalities, features, and significant advantages of SenseAnywhere products, making a compelling case for their integration into any facility prioritizing product safety, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency.
SenseAnywhere Product Overview
SenseAnywhere’s suite of monitoring solutions is engineered for effortless installation, use, and upkeep, boasting an impressive maintenance-free lifespan of up to a decade. These products, including the advanced AiroSensors, offer a seamless experience from the moment of deployment, automatically logging location arrival and departure times. An integrated accelerometer enhances the system’s capabilities by detecting motion or shock, with an optional feature for humidity monitoring, ensuring a comprehensive environmental overview.
Key Features:
- Extended Wireless Range: AiroSensors can wirelessly transmit data across 600 meters (with line of sight) to an AccessPoint, ensuring consistent data collection even in remote areas.
- Robust Data Logging: With a capacity for 18,500 event logs and 1,000,000 measurements, these devices offer unparalleled data recording capabilities.
- Real-Time Alerts: In the event of deviations from set temperature or storage time parameters, SenseAnywhere provides immediate notifications via email or SMS, safeguarding product quality and effectiveness.
- Compact, durable wireless data loggers: Certifications from NIST or equivalent accreditation.
- Installation-free setup: No wiring or button-pressing necessary for operation.
- Precise temperature measurements: Within ±0.10 C (0 to 70 C) and ±0.15 C (minus 40 to 0 C), with less than 0.01 C/year drift.
- User-friendly online platform: Requires no software installation, offering customizable reporting options.
- Immediate access to data: Stored securely in the cloud for a minimum duration of five years.
- Automated report generation process: Eliminating the need for manual input and ensuring data authenticity.
- Reports available in both tabular and graphical formats: Compliant with 21 CFR Part 11 standards.
- Facility Mapping: Streamlined and resource-efficient temperature mapping process.
Advanced Client Portal and Compliance Tools
SenseAnywhere’s client portal stands out as a pivotal tool for device management, allowing users to configure settings, set alarm profiles, and access comprehensive audit trails. This validated software adheres to GxP regulations, offering a full validation package to ensure GxP compliance, including design qualification, manufacturer software validation, installation qualification, and operational qualification.
Compliance and Certification:
SenseAnywhere’s approach to information security and quality management systems meets stringent regulatory requirements, facilitating the setup of a GxP-compliant temperature-monitoring solution. This commitment to compliance is further evidenced by the provision of NIST-traceable or accredited calibration certificates for its data loggers.
Innovations in Temperature Mapping and Laboratory Monitoring
SenseAnywhere revolutionizes GMP-compliant mapping studies with its real-time wireless temperature mapping tools. These tools are characterized by their accuracy, reliability, and minimal long-term drift, ensuring confidence in mapping studies and facilitating the efficient and error-free generation of mapping reports.
Laboratory Monitoring:
For facilities within the medical and pharmaceutical sectors, SenseAnywhere offers round-the-clock protection, aligning with FDA standards for safety and traceability. The system’s data loggers meticulously record environmental conditions, providing immediate alerts for any discrepancies, thus ensuring the continuous safety and efficacy of stored products.
The Investment Argument
Investing in SenseAnywhere’s monitoring solutions is a strategic decision that transcends mere operational enhancement. It represents a commitment to maintaining the highest standards of product integrity, regulatory compliance, and safety. The long-term benefits include:
- Risk Mitigation: The system’s real-time alerting capability significantly reduces the risk of product spoilage or loss due to environmental deviations.
- Regulatory Adherence: SenseAnywhere’s commitment to compliance ensures that facilities meet the most rigorous regulatory standards, safeguarding against potential legal and financial consequences.
- Operational Efficiency: The simplicity of installation, ease of use, and minimal maintenance requirements translate to reduced operational costs and enhanced efficiency, allowing staff to focus on core responsibilities rather than routine checks.
ARES Scientific: Elevating Pharmaceutical Manufacturing with Advanced SenseAnywhere Monitoring Solutions
In the intricate world of pharmaceutical manufacturing, where precision, reliability, and compliance are non-negotiable, ARES Scientific emerges as a beacon of expertise and innovation. As a distinguished provider in the industry, ARES Scientific offers a comprehensive suite of solutions tailored to meet the rigorous demands of pharmaceutical production environments. Among its exemplary offerings, the SenseAnywhere product line stands out, offering unparalleled monitoring capabilities for temperature, humidity, and CO2 levels.
With ARES Scientific, facilities gain access to advanced monitoring technology that ensures optimal conditions are maintained throughout the manufacturing process, safeguarding product integrity and adhering to stringent regulatory standards. The SenseAnywhere line, known for its ease of use, precision, and reliability, integrates seamlessly into existing workflows, providing real-time data and alerts that enable proactive management of environmental conditions.
Choosing ARES Scientific as your partner in pharmaceutical manufacturing equips your facility with the tools necessary to excel in a competitive and highly regulated industry. The SenseAnywhere product line, through its advanced monitoring capabilities, represents just a fraction of ARES Scientific’s commitment to delivering cutting-edge solutions that enhance efficiency, ensure compliance, and ultimately contribute to the production of safe and effective pharmaceuticals.




