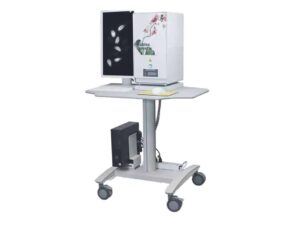
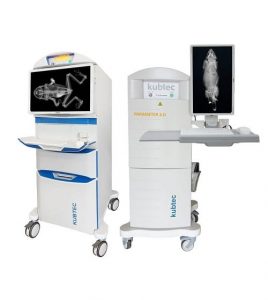
Cabinet X-Ray Systems for Research, Small-Animal Irradiation, NDT Inspection & Sterilization
Cabinet x-ray systems provide a self-contained, fully shielded enclosure for high-precision imaging, irradiation,
dosimetry, and non-destructive inspection—without the regulatory burden of open-beam or legacy gamma-source systems. These
cabinet x-ray systems—also called closed x-ray systems,
x-ray inspection cabinets, benchtop x-ray irradiators,
non-isotope x-ray irradiators, and shielded x-ray imaging systems—are widely used in
cell and tissue irradiation, small-animal irradiation,
medical device sterilization, blood product irradiation,
materials testing, NDT x-ray inspection, PCB/component evaluation,
security screening, and food/parcel contamination detection.
ARES Scientific offers systems ranging from compact benchtop irradiators to high-throughput, floor-standing shielded x-ray cabinets
with integrated x-ray tubes, flat-panel detectors, automated safety interlocks, and dose-monitoring software. These platforms support
laboratory workflows including preclinical radiation research, animal studies (mouse/rat),
cell/tissue irradiation, device and packaging sterilization,
industrial NDT radiography, electronics quality control, and
high-resolution cabinet x-ray imaging. Whether upgrading from a cesium or cobalt gamma irradiator or specifying a new
high-resolution cabinet system, the right platform delivers dose uniformity, regulatory compliance, operator safety, and
workflow efficiency.
Our experts help facilities compare essential specifications such as x-ray beam energy (kV),
dose rate and dose uniformity, shielding certification, cabinet size,
sample capacity, detector resolution, dosimetry features,
automated imaging controls, and throughput requirements.
Our cabinet systems integrate with categories including
x-ray irradiators and
shielded x-ray systems for a complete
radiation-processing solution.
Key Selection Factors for Cabinet X-Ray Systems
- Beam Energy & Dose Rate: Higher kV enables deeper penetration for thick materials, improved dose uniformity
for small-animal and cell irradiation, and higher-resolution imaging for NDT and inspection.
- Shielding & Regulatory Compliance: Self-shielded cabinets maintain exposure levels below
0.5 mR/h at 5 cm, meeting FDA cabinet x-ray standards and minimizing the need for room modifications.
- Cabinet Size & Sample Throughput: Select a chamber that accommodates your workflow, whether irradiating
animals, sterilizing devices, inspecting PCBs, imaging welds, or screening packages.
- Imaging, Software & Dosimetry: Modern systems feature flat-panel detectors,
real-time imaging, automated dose monitoring, turntables or rotating shelves,
data logging, and QA tools for repeatable research outcomes.
- Gamma/Cesium Source Replacement: Many institutions upgrade to cabinet x-ray systems to eliminate radioactive
materials, simplify security requirements, lower lifecycle costs, and improve dose control.
Frequently Asked Questions About Cabinet X-Ray Systems
1. What is a cabinet x-ray system?
A cabinet x-ray system is a fully enclosed, shielded machine in which the x-ray tube and sample chamber are housed inside a protective
enclosure, allowing safe operation without external shielding infrastructure.
2. What applications are cabinet x-ray systems used for?
Common uses include small-animal irradiation, cell/tissue studies,
device sterilization, NDT inspection, PCB evaluation,
materials testing, security screening, and food contamination detection.
3. How do cabinet x-ray systems differ from open-beam irradiators?
Cabinet systems are fully self-shielded, require minimal room modifications, reduce regulatory oversight, and offer safer and more
flexible irradiation or imaging workflows.
4. Can cabinet systems replace cesium or cobalt gamma irradiators?
Yes. Many facilities replace gamma irradiators with cabinet x-ray systems to eliminate radioactive sources, lower security burdens,
simplify disposal, and improve operational safety.
5. Are cabinet x-ray systems suitable for small-animal irradiation?
Absolutely. Many cabinets are optimized for preclinical research with features like dose uniformity,
adjustable staging, imaging guidance, and precise control over exposure parameters.
6. Can cabinet x-ray systems be used for medical device or packaging sterilization?
Yes. Certain models are engineered for high-throughput sterilization of devices, components, consumables, and
medical packaging, with validated dose monitoring.
7. Are cabinet x-ray systems appropriate for NDT and industrial inspection?
Yes. They are widely used for weld inspection, composite analysis,
part integrity checks, and electronics/PCB diagnosis.
8. What safety standards apply to cabinet x-ray systems?
In the U.S., FDA regulations require emissions below 0.5 mR/h at 5 cm. Cabinets also include interlocks,
fail-safes, warning lights, and dose monitoring for safe operation.
9. What features should I look for in imaging and detector technology?
Look for high-resolution flat-panel detectors, real-time imaging,
geometric magnification, motorized stages, and advanced software
for analysis and QA.
10. What industries commonly use cabinet x-ray systems?
Research labs, universities, vivariums, medical manufacturers, aerospace, electronics/PCB firms, food processing, security screening
facilities, and industrial NDT groups all rely on cabinet x-ray technology.