One of the many responsibilities of pharmacy technicians is the sterile compounding of hazardous drugs. This may be for compounds that are carcinogenic, genotoxic or teratogenic. The USP 797 and 800 handbook guides chemical and pharmaceuticals’ handling and storage requirements with biosafety considerations.1
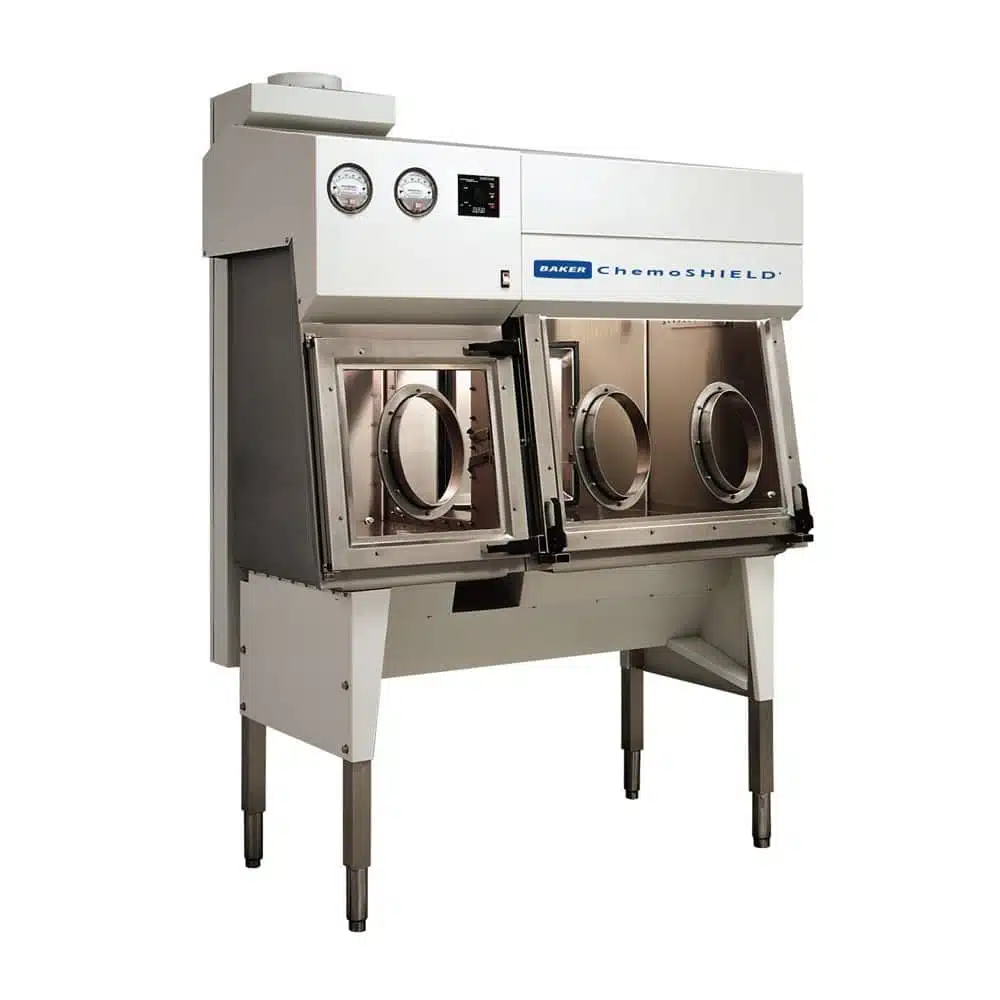
An important part of ensuring biosafety for hazardous compounding is the use of biological safety cabinets. An essential piece of pharmacy equipment, a biological safety cabinet can help protect pharmacy technicians and ensure safe compound handling.
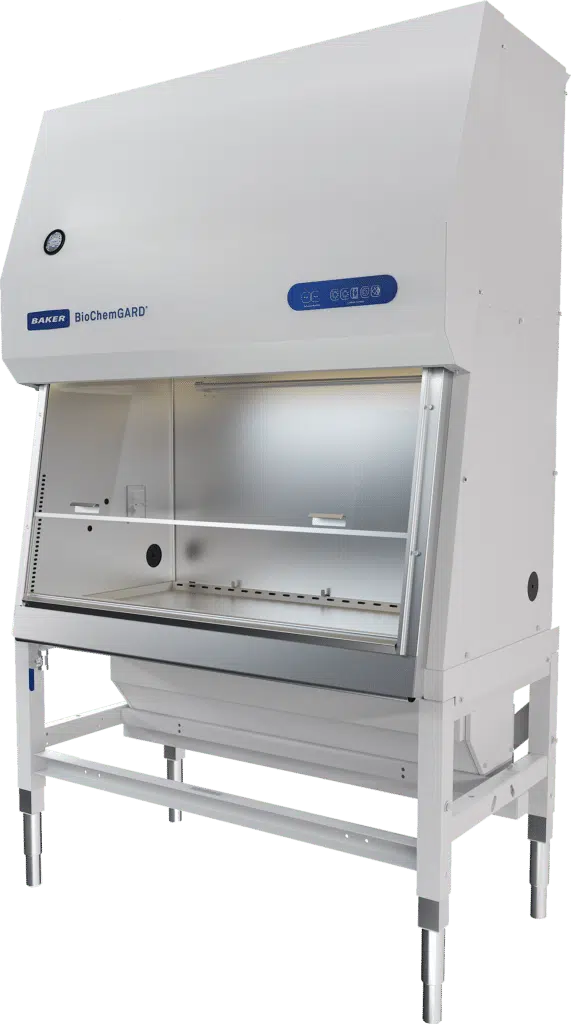
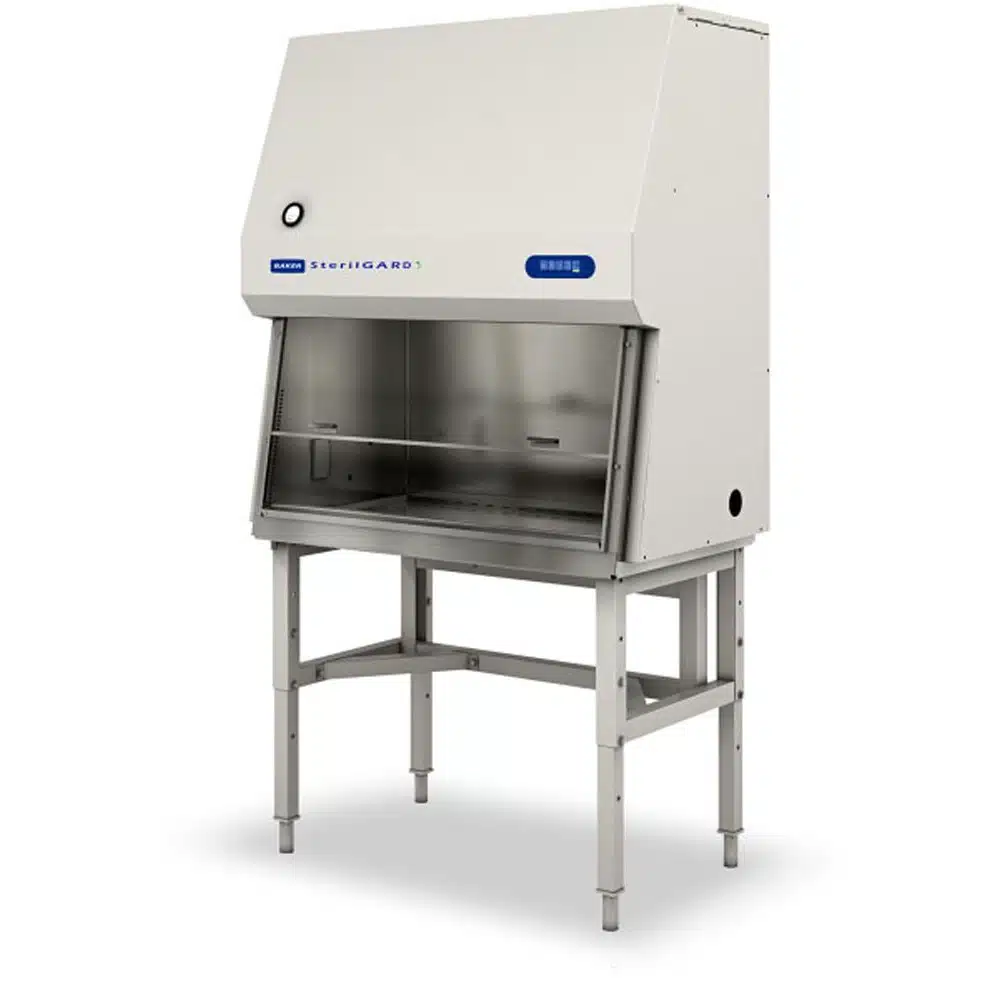
Which kind of biosafety cabinet is appropriate for hazardous compounding? Biosafety cabinets are divided into three classes, with class II protecting the operator and the compounds being handled. There are also two sub-types of class II biosafety cabinets, A2 and B2. B2 biosafety cabinets are suitable for handling radioactive substances and highly toxic chemicals as they are entirely vented. A2 cabinets use recirculated air.
Hazard Assessment
The most crucial step in assessing which biosafety cabinet is appropriate is to evaluate the risks of the chemical or pharmaceutical compounds that will be handled.2 The most affordable option is often a Class II A2 biological safety cabinet which is highly energy-efficient, recirculating, and can be outfitted with an exhaust canopy connection to provide exhaust capabilities.
Class II, B2 cabinets are 100% vented to exhaust, so they are suitable for handling more toxic and volatile compounds. Nearly all biosafety cabinets use HEPA filtration to help remove particulates and microorganisms from the air, whether it is being exhausted or recirculated.
The critical advantage of biosafety cabinets over fume hoods, that will remove toxic vapors, is that the biosafety cabinet provides an environment that is protective for the substance being handled as well as the user. This is very important in pharmacy environments where zero contamination of the compound can occur during the handling process. Many therapeutics will be packaged in sterile environments, but USP 800 covers both sterile and non-sterile compounding.1
Other considerations to ensure utmost safety, along with the biosafety cabinet design and level, are factors such as additional training and the use of containment rooms. While biosafety cabinets can be completely isolated environments, a ventilated room with negative pressure is still recommended to comply with USP 800. This is to act as a secondary contaminant measure. Staff must also know how to work in biosafety cabinets and follow safety protocols.
ARES Scientific
ARES Scientific offer a comprehensive range of biosafety cabinets, from walk-in containment enclosures to benchtop isolation systems. Each of these products is highly customizable, with low edition models available for rooms with low ceilings or additional electrical outlets as required.
To help you make the right choice and protect your staff’s wellbeing, ARES Scientific offers a free consultation service to help you find the biosafety cabinet that is right for your needs.
Whether you need a cabinet for fitting complex robotics in or a compact pharmacy cabinet for a limited amount of compounding work, ARES Scientific has the infrastructure for you.
Contact ARES Scientific today to find the right combination of biosafety cabinet features and class for you, whether you need to be handling microbiological samples, toxic chemicals or sterile pharmaceuticals.
References and Further Reading
- NIOSH (2022) USP800, https://www.usp.org/compounding/general-chapter-hazardous-drugs-handling-healthcare, accessed July 2022